Concepts to Constraints
Table of Contents
- Introduction to REST API
- Importance of API Design
- Elements of an Scalable API
- 6 Constraints of REST API
- A Good Looking API
- Measuring the API Maturity
What is REST API
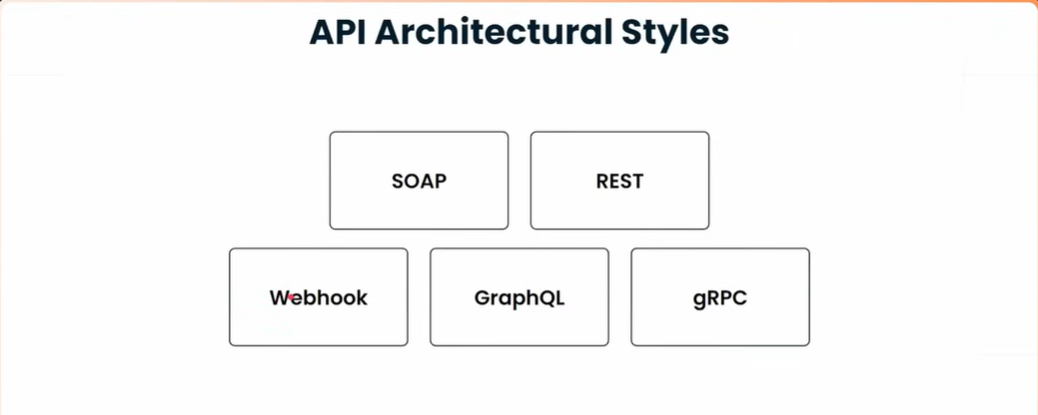
API Architectural Styles
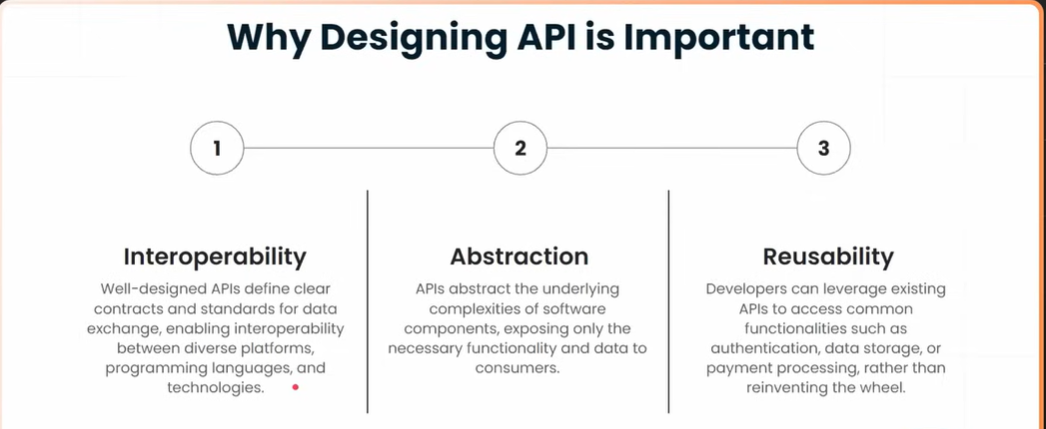
Why API Design is important

Explore real world examples
https://woocommerce.github.io/woocommerce-rest-api-docs/#introduction
https://docs.github.com/en/rest?apiVersion=2022-11-28
API Stakeholders
Two mail Stakeholders
- Producer
- Consumer like in a full stack application, backend app is producer and frontend is consumer
Lifecycle of an API
Constraints of REST API
- Client Server
- Statelessness
- Cacheability
- Uniform Interface
- Layered System
- Code on Demand
Client Server
The system should be divided into client and server components that are independent of each other. This separation allows for improved scalability and enables the client and server to evolve independently.
Statelessness
Each request from a client to the server must contain all the information necessary to understand and fulfill the request. The server should not maintain any client state between requests. If you manage user sessions in a RESTful API, you would be introducing statefulness into your architecture, which goes against the Statelessness constraint of REST. This constraint simplifies server design, improves reliability and supports better scalability.
Cacheability
Responses from the server should be explicitly labeled as cacheable or non-cacheable. Caching can improve performance and and reduce latency by allowing clients to reuse previously fetched responses.
two types of cahce : public and private, there should be a max age for the Caching.